Primary Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of Breast: an uncommon variant.
Keywords:
Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of breast, Endocrine tumor, Breast cancer, Histopathology
Abstract
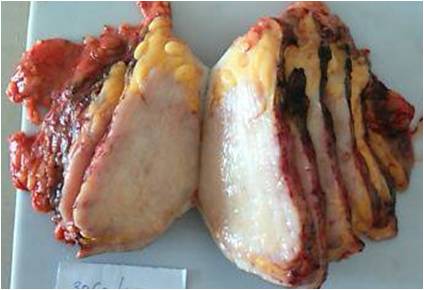
Neuroendocrine carcinoma of breast ( NECB) is an aggressive variant of invasive mammary carcinoma. Very few cases of Primary NECB have been reported in the literature. Here we report a 50 year female presented with left breast lump measuring 15 x 12 cm. of gradual onset with left axillary lymphadenopathy. On fine needle aspiration cytology of breast and lymphnode were positive for malignant cells. On ultrasonography of abdomino- pelvis showed metastasis to liver, peri pancreatic and para aortic lymph nodes with minimal ascites. On histopathology reported as Primary NECB-Large cell type-left breast. We are presenting this case for its extreme rarity and aggressive clinical behaviour. DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1094References
1) Zhang Y, Chen Z, Bao Y, Du Z, Li Q, Zhao Y, et al. Invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast: a prognostic research of 107 Chinese patients. Neoplasma 2013;60:215-22.
2) Kim JW, Woo OH, Cho KR, Seo BK, Yong HS, Kim A, et al. Primary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast: radiologic and pathologic findings. J Korean Med Sci 2008;23:1118-20.
3) Modlin IM, Lye K D, Kidd M. A five decade analysis of 13,715 carcinoid tumors. Cancer.2003;97:934-959.
4) David O, Bhattacharjee M. Diffuse neuroendocrine differentiation in a morphologically composite mammary infiltrating ductal carcinoma:a case report and review of literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med.2003;127(3):e131-4.
5) Ozbilim G, Kilicarslan B, Tezer E, Buyukkece A, Ustum M, Karaveli S et al. Breast carcinoma showing neuroendocrine differentiation characterized with ectopic hormone production (2 case report). Turk J Med Sci 2000;30:609-13.
6) Sapino A, Righi F, Cassoni P, Papitti M, Gugliotta P, Bussolati G. Expression of the neuroendocrine phenomenon in carcinoma of the breast. SeminDiagnPathol 2000;17:127-37.
7) Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Saste-Garau X. Invasive breast carcinoma. In: Tavassoli FA, Devilee P, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of the tumours of breast and female genital organs. Lyon: IARC press;2003:13-59.
8) Tovosoli FA, Pathology of the breast. 1st ed. Norwalk: Connecticut. Appleton and Lange;2000.
9) Wang Jun, Bing Wei, Constance TA, et al. Invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of breast: a population based study from the surveillance, epidemiology and end result (SEER) database, BMC cancer.2014;14:147.
10) Stita W, Trabelsi A, Gharbi O, Mokni M, Korbi S. Primary solid neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast Can J Surg 2009;52:E289-E290.
11) Hanna MY, Leung E, Rogers C, Pilgrim S. Primary large-cell neuroendocrine tumor of the breast. Breast J. 2013;19:204–206.
12) Wei B, Ding T, Xing Y, Wei W, Tian Z, Tang F, et al. Invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast: A distinctive subtype of aggressive mammary carcinoma. Cancer. 2010;116:4463–73.
2) Kim JW, Woo OH, Cho KR, Seo BK, Yong HS, Kim A, et al. Primary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast: radiologic and pathologic findings. J Korean Med Sci 2008;23:1118-20.
3) Modlin IM, Lye K D, Kidd M. A five decade analysis of 13,715 carcinoid tumors. Cancer.2003;97:934-959.
4) David O, Bhattacharjee M. Diffuse neuroendocrine differentiation in a morphologically composite mammary infiltrating ductal carcinoma:a case report and review of literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med.2003;127(3):e131-4.
5) Ozbilim G, Kilicarslan B, Tezer E, Buyukkece A, Ustum M, Karaveli S et al. Breast carcinoma showing neuroendocrine differentiation characterized with ectopic hormone production (2 case report). Turk J Med Sci 2000;30:609-13.
6) Sapino A, Righi F, Cassoni P, Papitti M, Gugliotta P, Bussolati G. Expression of the neuroendocrine phenomenon in carcinoma of the breast. SeminDiagnPathol 2000;17:127-37.
7) Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Saste-Garau X. Invasive breast carcinoma. In: Tavassoli FA, Devilee P, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of the tumours of breast and female genital organs. Lyon: IARC press;2003:13-59.
8) Tovosoli FA, Pathology of the breast. 1st ed. Norwalk: Connecticut. Appleton and Lange;2000.
9) Wang Jun, Bing Wei, Constance TA, et al. Invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of breast: a population based study from the surveillance, epidemiology and end result (SEER) database, BMC cancer.2014;14:147.
10) Stita W, Trabelsi A, Gharbi O, Mokni M, Korbi S. Primary solid neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast Can J Surg 2009;52:E289-E290.
11) Hanna MY, Leung E, Rogers C, Pilgrim S. Primary large-cell neuroendocrine tumor of the breast. Breast J. 2013;19:204–206.
12) Wei B, Ding T, Xing Y, Wei W, Tian Z, Tang F, et al. Invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast: A distinctive subtype of aggressive mammary carcinoma. Cancer. 2010;116:4463–73.
Published
2017-03-28
Issue
Section
Case Report
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




