Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Of Urinary Bladder
Keywords:
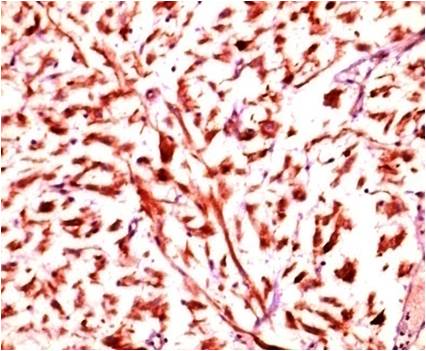
ALK 1 immunostain, Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, spindle myoepithelial cell proliferation.
Abstract
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is an uncommon benign tumor of intermediate neoplastic potential, characterised by spindle cell proliferation with characteristic fibroinflammatory and pseudosarcomatous appearance. A subset of IMT with histologic atypia and/or clinical aggressiveness is also known. IMTs occur in the mesentery, omentum, retroperitoneum, pelvis, and abdominal soft tissues. However, the occurrence of IMT in urinary bladder is unusual. IMT exhibits morphologic and immunophenotypic overlap with malignant spindle cell tumors of the urinary bladder and is diagnostically challenging. In the case presented, ALK-1 and SMA immunostains helped to identify IMT. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene translocation or ALK gene expression can further confirm IMT. Complete surgical excision with follow-up is the treatment of choice for IMT. DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1129References
1. Etani T, Naiki T, Nagai T, Lida K, Ando R, Naiki-Ito A et al. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic tumor of urinary bladder; A case report. Case Rep Oncol 2016; 9(2) : 464-469
2. Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn P, Mertens F. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Vol. 5. Lyon : IARC Press ; 2013 ; 83–84.
3. Coffin CM, Hornick JL, Flethcher CD. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: Comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypicall and aggressive cases. Am J Sur Pathol 2007; 31(4): 509-520
4. Rao RN, Ranjan P, Singla N, Pandey R. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder diagnosed by anaplastic lymphoma kinase immunostaining. Urol Ann 2012; 4(2): 115-118
5. Dobrosz Z, Rys J, Palen P, Wlaszczuk P, Ciepiela M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder – an unexpected case co-existing with an ovarian teratoma. Diagnost Pathol 2014:9;138
6. Pettinano G, Manivel JL, De Rosa N, Dehner LP. IMT (plasma cell granuloma): Clinico-pathologic study of 20 cases with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural observations. Am J Clin Pathol 1990; 94: 538-546
7. Yagnik V, Chadha A, Chaudhari S, Patel K. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder. Urol Ann 2010; 2(2): 78-79
8. Mills SE. Editor. Sternberg’s Diagnostic Surgical Pathology. 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010
9. Zhao J, Ping H, Xing N. Post-operative spindle cell nodule of the bladder : a case report and review of literature. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7(5): 1507-1510
10. Toyonori T, Christina M, Jonathan E. ALK-1 Expression in Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Urinary bladder. Am J Sur Pathol 2004; 28(12): 1609-1614
11. Tanny SPT, Wang LL, Liddell HA, Longano A, Appu S, Shahbaz S. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder : a case report. Urol Case Rep 2016 ; 6: 58-59
2. Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn P, Mertens F. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Vol. 5. Lyon : IARC Press ; 2013 ; 83–84.
3. Coffin CM, Hornick JL, Flethcher CD. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: Comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypicall and aggressive cases. Am J Sur Pathol 2007; 31(4): 509-520
4. Rao RN, Ranjan P, Singla N, Pandey R. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder diagnosed by anaplastic lymphoma kinase immunostaining. Urol Ann 2012; 4(2): 115-118
5. Dobrosz Z, Rys J, Palen P, Wlaszczuk P, Ciepiela M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the bladder – an unexpected case co-existing with an ovarian teratoma. Diagnost Pathol 2014:9;138
6. Pettinano G, Manivel JL, De Rosa N, Dehner LP. IMT (plasma cell granuloma): Clinico-pathologic study of 20 cases with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural observations. Am J Clin Pathol 1990; 94: 538-546
7. Yagnik V, Chadha A, Chaudhari S, Patel K. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder. Urol Ann 2010; 2(2): 78-79
8. Mills SE. Editor. Sternberg’s Diagnostic Surgical Pathology. 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010
9. Zhao J, Ping H, Xing N. Post-operative spindle cell nodule of the bladder : a case report and review of literature. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7(5): 1507-1510
10. Toyonori T, Christina M, Jonathan E. ALK-1 Expression in Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Urinary bladder. Am J Sur Pathol 2004; 28(12): 1609-1614
11. Tanny SPT, Wang LL, Liddell HA, Longano A, Appu S, Shahbaz S. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the urinary bladder : a case report. Urol Case Rep 2016 ; 6: 58-59
Published
2017-03-28
Issue
Section
Case Report
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




