Platelet Volume Indices: Silver linings for vascular complications in diabetes mellitus
Keywords:
Platelet Volume Indices, Mean Platelet Volume, Platelet Distribution Width, IFG, HBA1c, Diabetes
Abstract
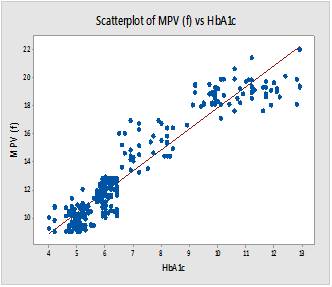
Background: Morbidity and mortality in diabetes owing to micro and macro angiopathic complications is well known. Platelet indices are potentially useful surrogate markers for early diagnosis of diabetic complications attributed to platelet activation and recognized by increase in Platelet Volume Indices (PVI) including Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) and Platelet Distribution Width (PDW). The aim is to determine and compare MPV and PDW in known cases of diabetics with and without diabetes related complications. To document changes in platelet indices with duration of diabetes and to assess utility of platelet indices in early identification of vascular complications especially in developing countries like India.Methods: A two year cross sectional study with total 330 individuals segregated into two groups:- (a)Diabetic subjects with diabetes related complications (b) Diabetic subjects without diabetes related complications. Samples for HbA1c and platelet indices were obtained and processed on SYSMEX-X-800i autoanalyser.Result: The study revealed significant positive correlation between PVI and duration of diabetes across the groups (MPV-HbA1c r = 0.951; PDW-HbA1c r = 0.875). MPV & PDW of subjects with and without diabetes related complications were (15.14 ± 1.04) fl & (17.51±0.39) fl and (18.96 ± 0.83) fl & (20.09 ± 0.98) fl respectively with a significant p value 0.00.Conclusion: The current study demonstrates raised platelet indices in association with rising glycaemic levels and diabetes related vascular complications. This is the first study of its kind in India which is comprehensive with an adequately powered study design. PVI should be researched and explored further as surrogate marker to develop a clinical tool for early recognition of diabetic vascular changes.References
1. Mahdavi et al. The effect of seeing a family physician on the level of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders 2013;12:2.
2. Ferroni P, Basili S. Platelet activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Thromb Haemost 2004;2:1282–1291.
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes care 2013;36(Supplement 1):S11-S66.
4. Khemka, R., Kulkarni, K. Study of relationship between Platelet Volume Indices and Hyperlipidemia. Annals Of Pathology And Laboratory Medicine, 2014;1(1), 8-14.
5. Zuberi BF. Comparison of mean platelet volume in patients with diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose and non-diabetic subjects. Singapore Medical Journal 2008;49(2):114-6.
6. Papanas N, Symeonidis G, Maltezos E. Mean platelet volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Platelets 2004;15:475-8.
7. Demirtunc R. The relationship between glycemic control and platelet activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications 2009;23(2):89-94.
8. Jindal S. Platelet indices in diabetes mellitus: indicators of diabetic microvascular complications. Hematology 2011;16(2):86-9.
9. Bhayana A. Is large platelet size a risk factor for acute coronary syndrome: A retrospective case-control study. J MGIMS, 2009 Sep;14(ii):52-55.
10. Farah Jabeen. Role of platelet indices, glycemic control and hs-CRP in pathogenesis of vascular complications in type-2 diabetic patients. Pak J Med Sci 2013;29(1):152-156.
11. Kim KY. Mean platelet volume in the normal state and in various clinical disorders. Yonsei Medical Journal 1986;27(3).
12. Khandekar MM, Khurana AS. Platelet volume indices in patients with coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction: an Indian scenario. J Clin Pathol 2006;59:146–149.
13. Manchanda, J, Potekar R, Badiger S, Tiwari, A. The study of platelet indices in acute coronary syndromes. Annals Of Pathology And Laboratory Medicine, 2015;2(1), A30-A35.
2. Ferroni P, Basili S. Platelet activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Thromb Haemost 2004;2:1282–1291.
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes care 2013;36(Supplement 1):S11-S66.
4. Khemka, R., Kulkarni, K. Study of relationship between Platelet Volume Indices and Hyperlipidemia. Annals Of Pathology And Laboratory Medicine, 2014;1(1), 8-14.
5. Zuberi BF. Comparison of mean platelet volume in patients with diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose and non-diabetic subjects. Singapore Medical Journal 2008;49(2):114-6.
6. Papanas N, Symeonidis G, Maltezos E. Mean platelet volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Platelets 2004;15:475-8.
7. Demirtunc R. The relationship between glycemic control and platelet activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications 2009;23(2):89-94.
8. Jindal S. Platelet indices in diabetes mellitus: indicators of diabetic microvascular complications. Hematology 2011;16(2):86-9.
9. Bhayana A. Is large platelet size a risk factor for acute coronary syndrome: A retrospective case-control study. J MGIMS, 2009 Sep;14(ii):52-55.
10. Farah Jabeen. Role of platelet indices, glycemic control and hs-CRP in pathogenesis of vascular complications in type-2 diabetic patients. Pak J Med Sci 2013;29(1):152-156.
11. Kim KY. Mean platelet volume in the normal state and in various clinical disorders. Yonsei Medical Journal 1986;27(3).
12. Khandekar MM, Khurana AS. Platelet volume indices in patients with coronary artery disease and acute myocardial infarction: an Indian scenario. J Clin Pathol 2006;59:146–149.
13. Manchanda, J, Potekar R, Badiger S, Tiwari, A. The study of platelet indices in acute coronary syndromes. Annals Of Pathology And Laboratory Medicine, 2015;2(1), A30-A35.
Published
2016-10-11
Issue
Section
Original Article
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




