Intraoperative squash cytology of CNS and spinal cord lesions with histologic correlation
Keywords:
Central Nervous System, Histopathology, Squash cytology.
Abstract
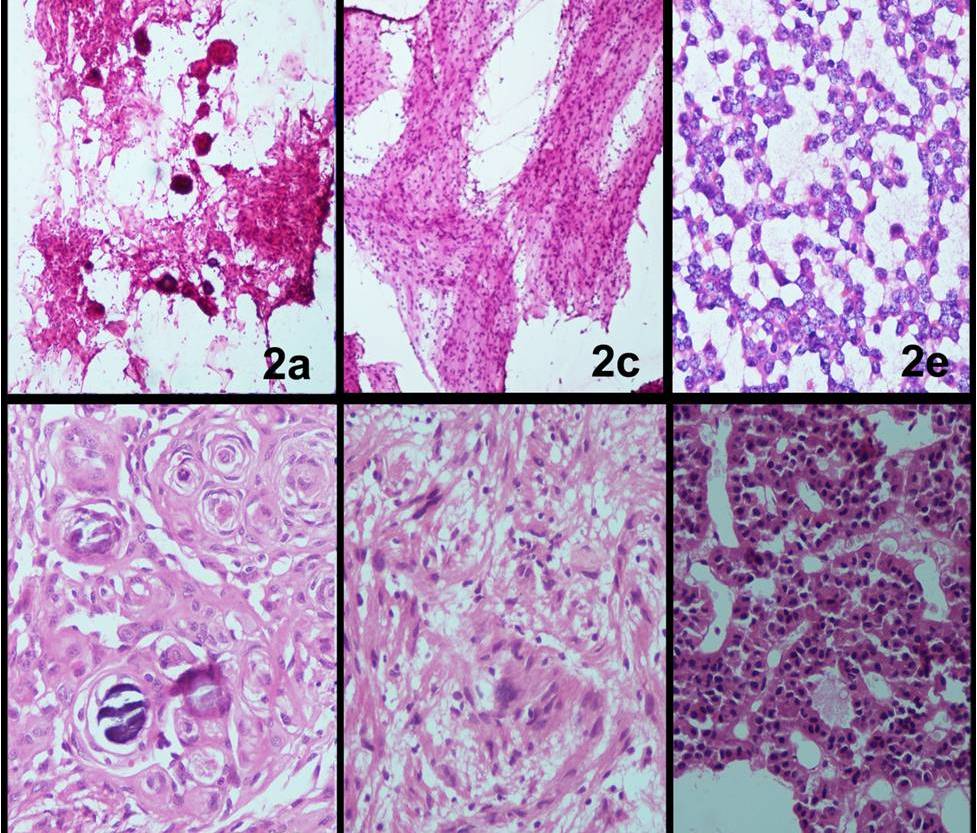
Background: Squash Cytology is now a well established and universally accepted technique in diagnosing a wide range of Central Nervous System (CNS) lesions and is presently being employed for both therapeutic and prognostic reasons. This study was conducted with an aim to correlate squash smears with histopathology and to compare statistical data employing sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy of squash cytology. Methods: The present study was a retrospective study comprising 369 lesions of central nervous system and spinal cord that were retrieved from archives. All the cases for which Intraoperative squash cytology and subsequent histopathology was available were included in the study. Cytology smears were stained with May- Grunwald- Geimsa (MGG), Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) and Pap stain. Histopathology smears were made from formalin fixed tissue sent separately and stained with H&E.Results: Of 369 cases, 86.4% were neoplastic and 13.6% nonneoplastic on histopathology. Amongst neoplasms, Astrocytic tumors constituted 24.7% of cases followed by Meningiomas comprising 17.8%. Amongst the benign lesions Tuberculoma was seen most frequently (3.25%). Overall diagnosticAccuracy of squash was 95.25%. On statistical analysis Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive value (PPV) and Negative Predictive Value (NPV) of squash cytology were 94.3%, 95.6%, 95.3% and 95.1% respectively. On applying student T test, for statistical correlation between squash cytology and histopathology p value was 0.363347 (p>0.05) hence errors in diagnosis by squash were insignificant. Conclusion: Intraoperative squash cytology is fairly accurate, reliable and cost effective method for rapid diagnosis of CNS lesions.References
1. Silverberg SG, De Lellis RA, Frable WJ, Li Volsi VA, Wick MR. Silverberg’s principles and practice of surgical pathology and cytopathology. 4th ed.Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2006.
2. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ. Unreliability of contemporary neurodiagnostic imaging in evaluating suspected adult supratentorial (low grade) astrocytoma. Journal of Neurosurgery 1993;79(4):533-36.
3. Cappabinaca P,Spaziante R,Caputi F et al. Accuracy of the analysis of multiple small fragments of glial tumours obtained by stereotactic biopsy. Acta Cytol 1991,35:505-11.
4. Roessler K,Dietrich W,Kitz K. High Diagnostic Accuracy of Cytologic smears of Central Nervous Tumors. A 15- year experience based on 4172 patients. Acta Cytol 2002; 46:664-7.
5. Torres LF, Noronha LD, Gugelmin ES et al. Accuracy of smear technique in the cytological diagnosis of 650 lesions of the central nervous system. Diagn Cytopathology 2001;24:293-95.
6. Eisenhardt L, Cushing H. Diagnosis of intracranial tumor by supravital technique. Am J Pathol 1930;6(5):641-52.
7. Who classification of tumours of CNS edited by David N Louis et al, 4th edition 2007.
8. Klienhues P, Vol B, Anagnostopoulos J, Kiessnlg M. Morphological evaluation of Stereotactic brain tumour biopsies. Neuro chirurgica Suppl. 1984;33:171-81.
9. Feiden W, Bise K, Steude U, Pfister HN, Molter AA. The sterotactic brain biopsy of focal intracerebral lesion in AIDS patient . Acta Neurol Scand 1993;87:228-33.
10. Mouriquand C, Benabid AL, Breyton M. Stereotactic cytology of brain tumours: review of an eight year experience. Acta Cytol 1991,31:756-64.
11. Kontozoglu TE, Cramer HM. The advantage of intraoperative cytology: Analysis of 215 smears and review of the literature. Acta Cytol 1991;35:154-64.
12. Eric Piaton. Cytology of tumour of Central Nervous System: letters to the editors. Acta Cytol 1996;40:846-48.
13. Deshpande K, Sarase S, Shedge R, D’ costa G, Bharambe B. Accuracy and Diagnostic Yield of Intraoperative Squash Smear Technique in the Rapid diagnosis of CNS lesions. Bombay Hospital Journal 2010;52(2):153-60.
14. Nguyen Gk, Johnson ES, Mielke BW. Cytology of Neuroectodermal tumours of the brain in crush preparation: A review of 56 cases of deep seated tumours sampled by CT-guided sterotactic needle biopsy. Acta Cytol 1989;33:67-75.
15. Sharma N, Misra V, PA Singh, Gupta SK, Debnath S, Nautiyal A. Comparitive Efficacy of Imprint and squash Cytology in Diagnosing Lesions of the Central Nervous System. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 2011;12:1693-96.
16. Pawar N, Deshpande K, Sarase S, D’ costa G, Balgi S, Goel A. Evaluation of the squash smear Technique in the Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous Tumours: A cytomorphological Study. The Internet Journal of Pathology ;11:1.
17. Sidway MK, Jannilla FS. Intraoperative cytological diagnosis of lesions of central nervous system. AJCP 1997;108:56-66.
18. Iqbal M, Shah A, Wani MA, Kirmani A, Ramzan A. Utility of Crush Smear cytology in Intraoperative Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Lesions. Acta Cytol 2006;57:608-16.
19. Jaiswal S, Jaiswal AK, Behari S et al. Intraoperative squash cytology of central nervous system lesions: A single center study of 326 cases. Diag Cytopathol 2010;40(2):104-12.
20. Marshall LF, Adams H, Doyle D, Graham DI. The histological accuracy of the smear technique for neurosurgical biopsies. J Neurosurg 1973;39:82-8.
21. Bonner JM. Central Nervous System. In: intraoperative cytology. An adjunct to frozen section. Edited by JA Welkerson, JM Bonner, New York; Igaki-Shoin;1989:p.119
22. Ho-Keing Ng. Cytological feature of Ependymomas in smear preperations. Acta Cytol 1994;38:331-34.
23. Teo J, Ho- Keung Ng. Cytodiagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma in smear preperations. Acta Cytol 1998;42:673-78.
24. Kobayashi S. Meningiomas, neurilemmoma and astrocytoma specimens obtained with the squash method for cytodiagnosis. A cytological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Cytol 1993;37:913-22.
25. Folkerth RD. Smears and Frozen section in intraoperative diagnosis of CNS lesions. Neuro Surg Clin N Am 1994;5(1):1-18.
26. Goeld D, Sundaram C, Paul TR et al. Intraoperative cytology (squash smear) in neurosurgical practice- pitfalls in diagnosis experience based on 3057 samples from single institution. Cytopathology Official Journal of the British Society for Clinical Cytology.2007;18(5):300-8.
27. Ud Din N, Memon A, Idress R, Ahmad Z, Hasan S. Central nervous system lesions: correlation of intraoperative and final diagnosis, six year experience at a referral centre in developing country,Pakistan. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Preservation: APJCP 2011;12(6):1435-37.
28. Burger PC, Scheithaein BW, Vogel FS. Ed. Surgical Pathology of the Nervous System and its coverings. 4th ed, London:Churchill Livingstone;2002:p.122-26.
29. Smith AR, Eisheik TM, Silverman JF. Intraoperative cytologic diagnosis of supra sellar and sellar cystic lesion. Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:137-47.
30. Willems JG, Alva-Willems JM. Accuracy of cytologic diagnosis of central nervous system neoplasms in stereotactic biopsies. Acta Cytol 1984;28:243-9.
2. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ. Unreliability of contemporary neurodiagnostic imaging in evaluating suspected adult supratentorial (low grade) astrocytoma. Journal of Neurosurgery 1993;79(4):533-36.
3. Cappabinaca P,Spaziante R,Caputi F et al. Accuracy of the analysis of multiple small fragments of glial tumours obtained by stereotactic biopsy. Acta Cytol 1991,35:505-11.
4. Roessler K,Dietrich W,Kitz K. High Diagnostic Accuracy of Cytologic smears of Central Nervous Tumors. A 15- year experience based on 4172 patients. Acta Cytol 2002; 46:664-7.
5. Torres LF, Noronha LD, Gugelmin ES et al. Accuracy of smear technique in the cytological diagnosis of 650 lesions of the central nervous system. Diagn Cytopathology 2001;24:293-95.
6. Eisenhardt L, Cushing H. Diagnosis of intracranial tumor by supravital technique. Am J Pathol 1930;6(5):641-52.
7. Who classification of tumours of CNS edited by David N Louis et al, 4th edition 2007.
8. Klienhues P, Vol B, Anagnostopoulos J, Kiessnlg M. Morphological evaluation of Stereotactic brain tumour biopsies. Neuro chirurgica Suppl. 1984;33:171-81.
9. Feiden W, Bise K, Steude U, Pfister HN, Molter AA. The sterotactic brain biopsy of focal intracerebral lesion in AIDS patient . Acta Neurol Scand 1993;87:228-33.
10. Mouriquand C, Benabid AL, Breyton M. Stereotactic cytology of brain tumours: review of an eight year experience. Acta Cytol 1991,31:756-64.
11. Kontozoglu TE, Cramer HM. The advantage of intraoperative cytology: Analysis of 215 smears and review of the literature. Acta Cytol 1991;35:154-64.
12. Eric Piaton. Cytology of tumour of Central Nervous System: letters to the editors. Acta Cytol 1996;40:846-48.
13. Deshpande K, Sarase S, Shedge R, D’ costa G, Bharambe B. Accuracy and Diagnostic Yield of Intraoperative Squash Smear Technique in the Rapid diagnosis of CNS lesions. Bombay Hospital Journal 2010;52(2):153-60.
14. Nguyen Gk, Johnson ES, Mielke BW. Cytology of Neuroectodermal tumours of the brain in crush preparation: A review of 56 cases of deep seated tumours sampled by CT-guided sterotactic needle biopsy. Acta Cytol 1989;33:67-75.
15. Sharma N, Misra V, PA Singh, Gupta SK, Debnath S, Nautiyal A. Comparitive Efficacy of Imprint and squash Cytology in Diagnosing Lesions of the Central Nervous System. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 2011;12:1693-96.
16. Pawar N, Deshpande K, Sarase S, D’ costa G, Balgi S, Goel A. Evaluation of the squash smear Technique in the Rapid Diagnosis of Central Nervous Tumours: A cytomorphological Study. The Internet Journal of Pathology ;11:1.
17. Sidway MK, Jannilla FS. Intraoperative cytological diagnosis of lesions of central nervous system. AJCP 1997;108:56-66.
18. Iqbal M, Shah A, Wani MA, Kirmani A, Ramzan A. Utility of Crush Smear cytology in Intraoperative Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Lesions. Acta Cytol 2006;57:608-16.
19. Jaiswal S, Jaiswal AK, Behari S et al. Intraoperative squash cytology of central nervous system lesions: A single center study of 326 cases. Diag Cytopathol 2010;40(2):104-12.
20. Marshall LF, Adams H, Doyle D, Graham DI. The histological accuracy of the smear technique for neurosurgical biopsies. J Neurosurg 1973;39:82-8.
21. Bonner JM. Central Nervous System. In: intraoperative cytology. An adjunct to frozen section. Edited by JA Welkerson, JM Bonner, New York; Igaki-Shoin;1989:p.119
22. Ho-Keing Ng. Cytological feature of Ependymomas in smear preperations. Acta Cytol 1994;38:331-34.
23. Teo J, Ho- Keung Ng. Cytodiagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma in smear preperations. Acta Cytol 1998;42:673-78.
24. Kobayashi S. Meningiomas, neurilemmoma and astrocytoma specimens obtained with the squash method for cytodiagnosis. A cytological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Cytol 1993;37:913-22.
25. Folkerth RD. Smears and Frozen section in intraoperative diagnosis of CNS lesions. Neuro Surg Clin N Am 1994;5(1):1-18.
26. Goeld D, Sundaram C, Paul TR et al. Intraoperative cytology (squash smear) in neurosurgical practice- pitfalls in diagnosis experience based on 3057 samples from single institution. Cytopathology Official Journal of the British Society for Clinical Cytology.2007;18(5):300-8.
27. Ud Din N, Memon A, Idress R, Ahmad Z, Hasan S. Central nervous system lesions: correlation of intraoperative and final diagnosis, six year experience at a referral centre in developing country,Pakistan. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Preservation: APJCP 2011;12(6):1435-37.
28. Burger PC, Scheithaein BW, Vogel FS. Ed. Surgical Pathology of the Nervous System and its coverings. 4th ed, London:Churchill Livingstone;2002:p.122-26.
29. Smith AR, Eisheik TM, Silverman JF. Intraoperative cytologic diagnosis of supra sellar and sellar cystic lesion. Diagn Cytopathol 1999;20:137-47.
30. Willems JG, Alva-Willems JM. Accuracy of cytologic diagnosis of central nervous system neoplasms in stereotactic biopsies. Acta Cytol 1984;28:243-9.
Published
2016-05-07
Issue
Section
Original Article
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




