Cytodiagnosis of Schwannoma of parotid gland: a rare entity in a child
Keywords:
Parotid, schwannoma, FNAC, cytological findings
Abstract
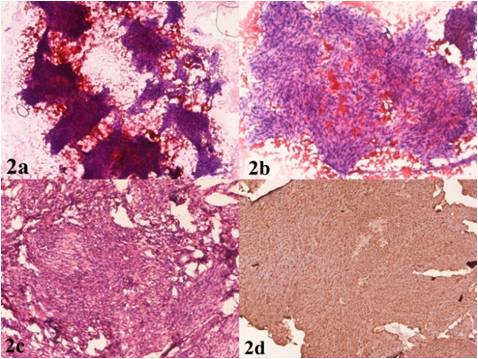
Schwannoma of parotid gland in a child is rare. We report a rare case of schwannoma in parotid gland in a 10-year-old child who presented with a gradually enlarging swelling in parotid region for the last I year. Color doppler study showed increased vascularity in the lesion with venous return pattern, suggestive of a hemangioma. However, fine needle aspiration cytology showed features consistent with schwannoma, comprising of sheets of uniform spindled cells with nuclei having tapering ends and exhibiting subtle nuclear palisading within a hypocellular fibrillary stromal background. The parotid mass was then excised. Histopathological and immuno- histochemical examinations further yielded the diagnosis of schwannoma, confirming the cytological diagnosis. This case report emphasizes that the cytodiagnosis of schwannoma is difficult due to many pitfalls encountered in fine needle aspirate. Therefore, schwannoma should always be considered in differential diagnosis of spindle-cell lesion in salivary glands even in children for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Unless schwannoma is included in the cytologic differential diagnosis, the surgeon may fail to recognize it at operation and may inadvertently transect the facial nerve.References
1. Oncel S, Onal K, Ermete M, Uluc E. Schwannoma (neurilemmoma) of the facial nerve presenting as a parotid mass. J LaryngolOtol 2002;116:642–3.
2. Jain R, Gupta S, Borkataky S, Agarwal R, Singh S, Gupta K et al. Rare Diagnosis on aspiration cytology of parotid gland schwannoma. ActaCytol 2010;54:112-4.
3. Henke CA, Salomao DR, Hughes JH. Cellular schwannoma mimics a sarcoma: an example of a potential pitfall in aspiration cytodiagnosis. DiagnCytopathol 1999;20:312-6.
4. Chhieng DC, Cohen JM, Cangiarella JF. Fine-needle aspiration of spindle cell and mesenchymal lesions of the salivary glands. DiagnCytopathol 2000;23:253–9.
5. Hui-Chi KU, Chi–Wei Yeh. Cervical Schwannoma. A case report and eight years review. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2000;114(6):414–7.
6. Falcioni M, Russo A, Taibah A, Sanna M. Facial nerve tumors. OtolNeurotol 2003;24:942-7.
7. Yaman H, Gerek M, Tosun F, Deveci S, Kiliç E, Arslan HH. Myoepithelioma of the parotid gland in a child: a case report. J PediatrSurg2010;45:E5-7.
8. Politi M, Toro C, Zerman N, Mariuzzi L, Robiony M. Myoepithelioma of the parotid gland: Case report and review of literature. Oral Oncology Extra 2005;41:104-8.
9. Saad RS, Takei H, Lipscomb J, Ruiz B. Nodular fasciitis of parotid region: a pitfall in the diagnosis of pleomorphic adenomas on fine-needle aspiration cytology. DiagnCytopathol2005;33:191-4.
10. Peng WX, Kudo M, Yamamoto T, Inai S, Fujii T, Teduka K et al. Nodular fasciitis in the parotid gland: a case report and review of the literature. DiagnCytopathol2013;41:829–33.
11. Iyer VK. Cytology of soft tissue tumors: Benign soft tissue tumors including reactive, nonneoplastic lesions. J Cytol 2008;25:81-6
12. Bauer JL, Miklos AZ, Thompson LD. Parotid gland solitary fibrous tumor: a case report and clinicopathologic review of 22 cases from the literature. Head Neck Pathol2012;6:21-31
13. Tao LC, Davidson DD. Aspiration biopsy cytology of smooth muscle tumors. A cytologic approach to the differentiation between leiomyosarcoma and leiomyoma. ActaCytol 1993;37:300-8.
2. Jain R, Gupta S, Borkataky S, Agarwal R, Singh S, Gupta K et al. Rare Diagnosis on aspiration cytology of parotid gland schwannoma. ActaCytol 2010;54:112-4.
3. Henke CA, Salomao DR, Hughes JH. Cellular schwannoma mimics a sarcoma: an example of a potential pitfall in aspiration cytodiagnosis. DiagnCytopathol 1999;20:312-6.
4. Chhieng DC, Cohen JM, Cangiarella JF. Fine-needle aspiration of spindle cell and mesenchymal lesions of the salivary glands. DiagnCytopathol 2000;23:253–9.
5. Hui-Chi KU, Chi–Wei Yeh. Cervical Schwannoma. A case report and eight years review. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2000;114(6):414–7.
6. Falcioni M, Russo A, Taibah A, Sanna M. Facial nerve tumors. OtolNeurotol 2003;24:942-7.
7. Yaman H, Gerek M, Tosun F, Deveci S, Kiliç E, Arslan HH. Myoepithelioma of the parotid gland in a child: a case report. J PediatrSurg2010;45:E5-7.
8. Politi M, Toro C, Zerman N, Mariuzzi L, Robiony M. Myoepithelioma of the parotid gland: Case report and review of literature. Oral Oncology Extra 2005;41:104-8.
9. Saad RS, Takei H, Lipscomb J, Ruiz B. Nodular fasciitis of parotid region: a pitfall in the diagnosis of pleomorphic adenomas on fine-needle aspiration cytology. DiagnCytopathol2005;33:191-4.
10. Peng WX, Kudo M, Yamamoto T, Inai S, Fujii T, Teduka K et al. Nodular fasciitis in the parotid gland: a case report and review of the literature. DiagnCytopathol2013;41:829–33.
11. Iyer VK. Cytology of soft tissue tumors: Benign soft tissue tumors including reactive, nonneoplastic lesions. J Cytol 2008;25:81-6
12. Bauer JL, Miklos AZ, Thompson LD. Parotid gland solitary fibrous tumor: a case report and clinicopathologic review of 22 cases from the literature. Head Neck Pathol2012;6:21-31
13. Tao LC, Davidson DD. Aspiration biopsy cytology of smooth muscle tumors. A cytologic approach to the differentiation between leiomyosarcoma and leiomyoma. ActaCytol 1993;37:300-8.
Published
2016-11-05
Section
Case Report
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




