Lymphadenosis benigna cutis or Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia- a rare case report
Keywords:
Lymphadenosis benigna cutis, Lymphocytoma cutis, pseudolymphomas.
Abstract
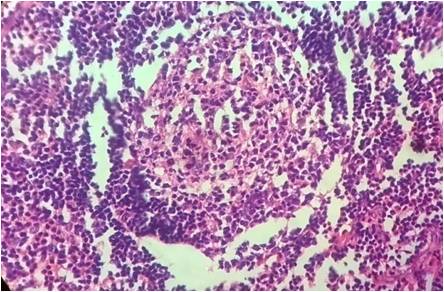
Lymphadenosis benigna cutis or cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia or lymphocytoma cutis or pseudolymphoma is classified as one of the inflammatory disorder in which accumulation of lymphocytes on skin resemble, clinically and histologically as, cutaneous lymphomas. It manifests as asymptomatic, indolent, nodular lesions of different sizes varying between 2 and 5 cm, usually solitary, mainly on exposed areas of the body like face and neck. The presence of polymorphous cell infiltrates comprising of T and B lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils, histiocytes and dendritic cells along with lack of atypical lymphocytes after incisional biopsy support diagnosis of pseudolymphoma. We report a 25 year old man who presented with bilateral postauricular swellings. The diagnosis was made as lymphocytoma cutis histologically and confirmed by immunohistochemistry. We report this case due to its distinct presentation and rarity of site and unusual size.References
1.Stacey E Millis, Darryl Carter, Joel K Greenson. Sternberg`s Diagnostic Surgical Pathology.5th ed vol I.Philadelphia, Wolter Kluwer/Lippincortt Williams & Wilkins;2010.p.64
2.Caro WA, Helwig EB: Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia.Cancer, 1969, 24:487-501
3. Arai E, Shimizu M, Hirose T. A review of 55 cases of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: reassessment of the histopathologic findings leading to reclassification of 4 lesions as cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and 19 as pseudolymphomatous folliculitis. Hum Pathol.2005;36:505-11.
4. Diaz-Cascajo C, Borghi S, Rey-Lopez A, Carretero-Hernandez G. Cutaneous lymphadenoma. A peculiar variant of nodular trichoblastoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996;18:186-91.
5. May SA, Netto G, Domiati-Saad R, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia and marginal zone B-cell lymphoma following vaccination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:512-516.
6.Roo E, Villegas C, Lopez Bran E, Jimenez E, Valle P, Sanchez Yus E. Postzoster cutaneous pseudolymphomas. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:661-3.
7. Bachelez H, Hadida F, Parizot C, Flageul B, Kemula M, Dubertret L et al. Oligoclonal expansion of HIV specific cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocytes in skin of HIV 1 infected patients with cutaneous pseudolymphoma. J Clin Invest 1998;101:2506-2516.
8.Lanzafame S, Micali G. [Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia(pseudolymphoma) secondary to vaccination]. Pathologica 1993;85:555-61.
9. Magro CM, Crowson AN. Drugs with antihistaminic property as a cause of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia. J Am Acad Dermatol 1995,32:419-28.
10. Ploysangam T, Breneman DL, Mutasim DF. Cutaneous pseudolymphomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;38:877-95;quiz 896-7.
11. Sampaio SAP, Rivitti EA. Dermatologia 3rd ed. Sao Paulo:Artes Medicas; 2007.p.1270-1.
12.Pecantha PLVB, Pereira Jr AC, Castro O. Diagnostico differential histopathologico e immune-hisquimico entre linforma maligne pseudolinfomas (linfocitoma): Estudo de tres casos. An Bras Dermatol.1995;70:319-21.
13. Kerl H et al. Primary cutaneous B cell lymphoma.Keio J Med 2001;50:269-273.
14. David Elder, Rosalie Elentisas, Bernett Johnson et al. Lever`s Histopathology of the Skin.9th ed. Philadelphia, Wolter Kluwer/Lippincortt Williams & Wilkins.2005.p.933.
15. Mackie RM: Cutaneous lymphomas and lymphocytic infiltrates. In Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, et al(eds).Textbook of dermatology, Vol 3,6th edition, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 2373-2402,1998.
2.Caro WA, Helwig EB: Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia.Cancer, 1969, 24:487-501
3. Arai E, Shimizu M, Hirose T. A review of 55 cases of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: reassessment of the histopathologic findings leading to reclassification of 4 lesions as cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma and 19 as pseudolymphomatous folliculitis. Hum Pathol.2005;36:505-11.
4. Diaz-Cascajo C, Borghi S, Rey-Lopez A, Carretero-Hernandez G. Cutaneous lymphadenoma. A peculiar variant of nodular trichoblastoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996;18:186-91.
5. May SA, Netto G, Domiati-Saad R, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia and marginal zone B-cell lymphoma following vaccination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:512-516.
6.Roo E, Villegas C, Lopez Bran E, Jimenez E, Valle P, Sanchez Yus E. Postzoster cutaneous pseudolymphomas. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:661-3.
7. Bachelez H, Hadida F, Parizot C, Flageul B, Kemula M, Dubertret L et al. Oligoclonal expansion of HIV specific cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocytes in skin of HIV 1 infected patients with cutaneous pseudolymphoma. J Clin Invest 1998;101:2506-2516.
8.Lanzafame S, Micali G. [Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia(pseudolymphoma) secondary to vaccination]. Pathologica 1993;85:555-61.
9. Magro CM, Crowson AN. Drugs with antihistaminic property as a cause of cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia. J Am Acad Dermatol 1995,32:419-28.
10. Ploysangam T, Breneman DL, Mutasim DF. Cutaneous pseudolymphomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998;38:877-95;quiz 896-7.
11. Sampaio SAP, Rivitti EA. Dermatologia 3rd ed. Sao Paulo:Artes Medicas; 2007.p.1270-1.
12.Pecantha PLVB, Pereira Jr AC, Castro O. Diagnostico differential histopathologico e immune-hisquimico entre linforma maligne pseudolinfomas (linfocitoma): Estudo de tres casos. An Bras Dermatol.1995;70:319-21.
13. Kerl H et al. Primary cutaneous B cell lymphoma.Keio J Med 2001;50:269-273.
14. David Elder, Rosalie Elentisas, Bernett Johnson et al. Lever`s Histopathology of the Skin.9th ed. Philadelphia, Wolter Kluwer/Lippincortt Williams & Wilkins.2005.p.933.
15. Mackie RM: Cutaneous lymphomas and lymphocytic infiltrates. In Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, et al(eds).Textbook of dermatology, Vol 3,6th edition, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 2373-2402,1998.
Published
25-02-2016
Issue
Section
Case Report
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access at http://opcit.eprints.org/oacitation-biblio.html).




